

Epigenetics refers to the phenomenon where the phenotype of an individual organism undergoes hereditary changes without altering the nucleotide sequence of the genome. DNA methylation is currently the most deeply studied epigenetic modification. In short, it refers to the chemical modification process in which an active methyl group is transferred to a specific base in the DNA strand under the catalysis of DNA methyltransferase, using S-adenosylmethionine as the methyl donor. In mammals, it mainly generates 5-methylcytosine (5-mC).

Figure 1- Under the action of DNA methylation catalytic enzyme (DNMT),The process of cytosine methylation

DNA methylation can occur at the C-5 position of cytosine, the N-6 position of adenine, the N-7 position of guanine, etc. They are respectively catalyzed by different DNA methylases to generate 5-methylcytosine (5-mC), n6-methyladenine (N6-mA), and 7-methylguanine (7-mG).
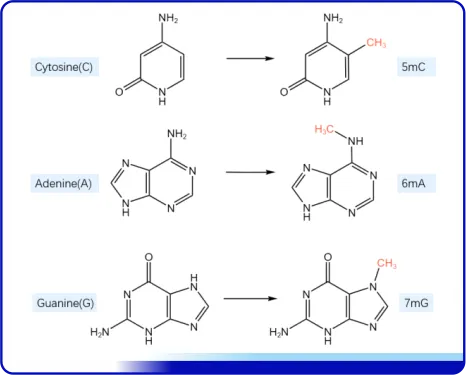
Figure 2- Schematic diagram of the location where methylation occurs in a base

Dam methylation: Methylation occurs at the adenine N6 position in the GATC sequence.
Dcm methylation: Methylation occurs at the C5 position of the second cytosine in the CCAGG and CCTGG sequences.
CpG methylation: In eukaryotes such as plants and mammals, the most common type of methylation that affects enzyme digestion is CpG methylation. CpG methyltransferase transfers methyl groups to the C5 position of cytosine residues.
When the methylation site overlaps with the restriction endonuclease recognition sequence, most enzymatic cuts will be blocked or affected.

Figure 3- Schematic diagram of methylation of dam, dcm, and CpG

Based on the methylation sensitivity of the above endonucleases, the partial methylation-sensitive restriction endonucleases were statistically classified as follows:

Note: The underlined part indicates the sequence recognized by the endonuclease, and the bases marked in color indicate the sequence that will undergo methylation modification.

With the discovery of DNA methylation, people have been constantly exploring how to conduct research on DNA methylation better and more conveniently. For organisms, alterations in methylation at gene loci may lead to changes in gene expression. Therefore, the study of methylation levels at loci is particularly important. At present, the commonly used method is to study the methylation level of individual sites by using methylation-sensitive enzymes to recognize and cut genomic DNA sequences.

Methyl-Sensitive Restriction Enzymes PCR: This method is quite ancient. Its principle is based on the characteristic that methylation-sensitive enzymes (such as HpaⅡ) are sensitive to the methylation of CG at the cleavage site. If the CG at the cleavage site is hypomethylated, it can be cleaved. After PCR amplification, there will be no band or the band will be very dark compared with the control. Conversely, if the CG at the cleavage site is hypermethylated, Then it will not be cut open. After PCR amplification, the band brightness is comparable to that of the control. The level of methylation at the site can be quickly determined through the results of electrophoresis. This method is simple to operate, has low cost and the results are easy to observe.

Figure 4- Detection of DNA methylation by methyl-sensitive restriction endonucleases
Based on the above methods, a more precise quantitative analysis of methylation has been developed, that is, fluorescence quantitative PCR (qPCR) is used to detect the substrates after methylation enzymatic digestion. PCR primers are designed upstream and downstream of the flanks of the target site. Undigested DNA can be used as a PCR template for amplification, while cleaved DNA theoretically cannot be amplified. The level of remaining undigested DNA depends on the methylation degree of the target site. The higher the methylation degree of the site, the fewer fragments can be cleaved by HpaII, and the more DNA templates are available for PCR amplification. DNA amplification can be detected earlier in qPCR (i.e., the lower the Ct value). Based on this principle, the methylation status of the site can be determined by qPCR analysis.
At present, the commonly used method is to study the methylation level of individual sites by using methylation-sensitive enzymes to recognize and cut genomic DNA sequences. Methylation-sensitive endonucleases have extensive applications in the field of methylation analysis and detection. The following figure shows the development history of methylation analysis methods, from liquid chromatography analysis to two-dimensional electrophoresis, and then to the application of third-generation sequencing technology in methylation analysis. Along with the continuous development of methylation sequencing technology, the methods of methylation sequencing involving methylation-sensitive endonucleases have also been constantly updated and iterated.
At present, the main applications are mostly concentrated in the pretreatment steps of samples. Through the combined analysis of various platforms such as sulfite sequencing and high-throughput sequencing, the methylation levels of the entire body and specific regions can be analyzed.
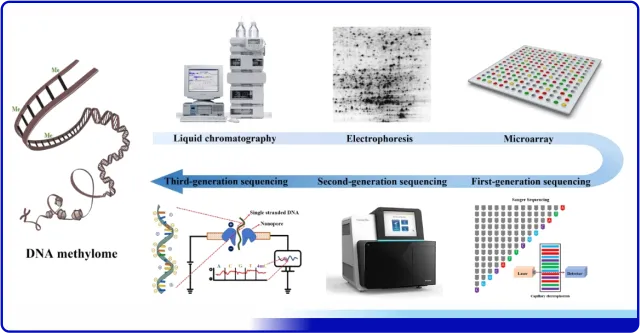
Figure 6- Detection of DNA methylation by methyl-sensitive restriction endonucleases

产品:HinP1Ⅰ, HhaⅠ, AciⅠ, HpaⅡ, BssHⅡ, BsrFⅠ, BspEⅠ.
Product features
Specificity: Enzymatic digestion has strong recognition specificity and the products are clear.
High efficiency: Verify that the enzymatic digestion efficiency is high. Reach or exceed imported products.
High fidelity: Overnight enzymatic digestion, with extremely low asterisk activity.
Experimental data
Conclusion
The Baorui methylation-sensitive endonuclease has a high digestion efficiency, clear digestion products, uniform bands of digestion products, and no non-specific cleavage, that is, no star activity phenomenon, reaching or surpassing the imported N Company products.

References
0756-8699969
Address: No. 88, Shuian 1st Road, Nanping Science and Technology Park, Xiangzhou District, Zhuhai City, Guangdong Province
Email: marketing@biori.com
Wechat official account |
Product consultation |
Join us |
Video Account |






